Artificial graphite is considered to be the most suitable material for the continuous or semi-continuous casting of non-ferrous metals. Production practice has proved that using graphite mould continuous casting industry, because of its good performance of thermal conductivity, thermal conductivity performance determines the speed of solidification of the metal or alloy), mold good self-lubricating performance factors, not only make the casting speed, and due to the size of the graphite blocks for casting precision, smooth surface, uniform crystal structure, can be directly for the next working procedure of processing. This not only greatly improves the rate of finished products, reduces the loss of waste, but also greatly improves the quality of products.
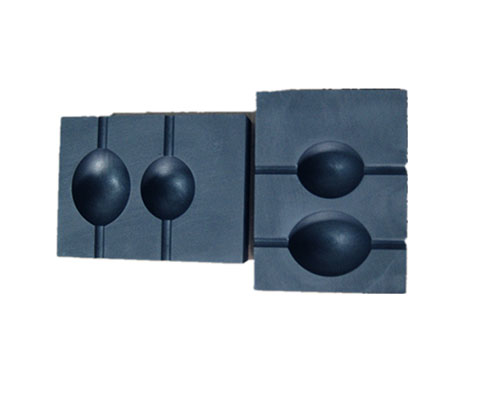
Graphite Mould for Casting Benefits
The coefficient of thermal expansion is an important factor to determine the use of graphite as die material. Molds are media with very heterogeneous temperatures, hot from the inside due to the molten material and cold from the outside due to the cooling process applied to them. The low thermal expansion coefficient exhibited by graphite enables the die to function without deformation or cracking. Another very important factor is self-lubrication. Graphite is a solid lubricant that creates low friction between the mold and the casting material. The graphite can then be smoothly extracted from the casting.
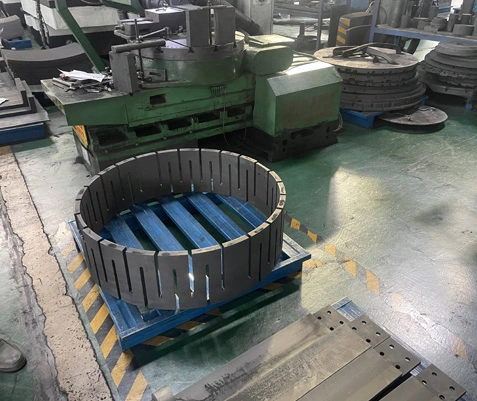
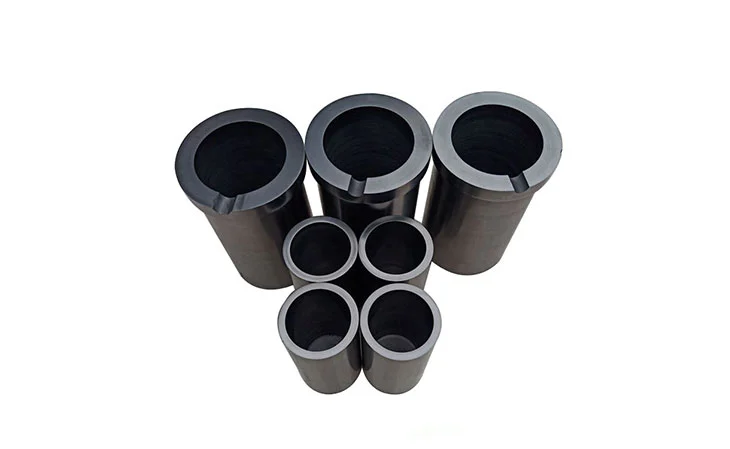
Isostatic graphite blocks and molded graphite blocks are key materials used in the casting industry, particularly for the production of high-quality and intricate metal components. These specialized graphite blocks play a crucial role in the manufacturing process by providing the necessary thermal stability, strength, and durability required for the precise formation of metal parts.
EDM Graphite blocks for casting
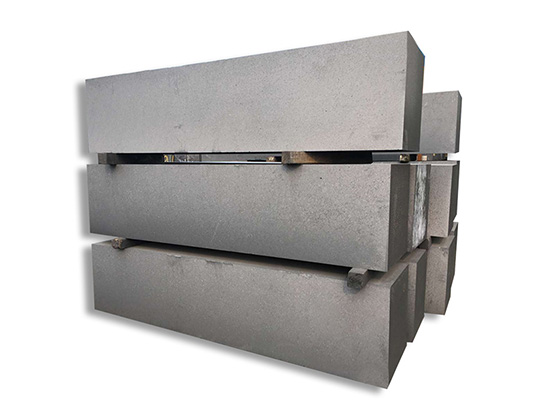
Isostatic Graphite blocks for casting
Isostatic graphite blocks are produced using a unique manufacturing process known as isostatic pressing, which involves subjecting graphite powder to high pressure from all directions. This results in a uniform density and excellent mechanical properties, making isostatic graphite blocks ideal for applications that demand high thermal shock resistance and dimensional stability.

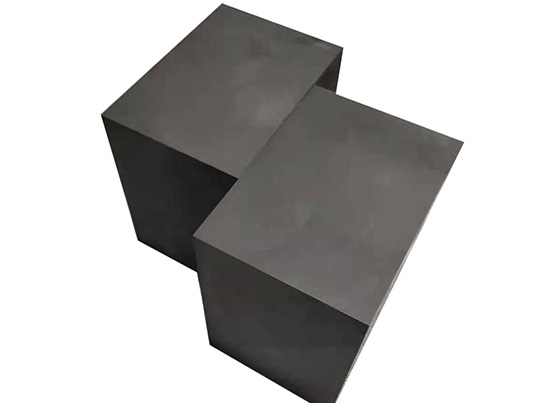
Molded Graphite blocks for casting
On the other hand, molded graphite block is created through a molding process that allows for the formation of complex shapes and sizes to suit specific casting requirements. Molded graphite blocks offer versatility and can be tailored to meet the exact specifications of the casting process, providing a cost-effective solution for producing intricate metal components with consistent quality.

Both types of graphite blocks excel in their ability to withstand extreme temperatures, making them suitable for use in various casting applications such as aluminum, copper, and other non-ferrous metal casting. Their excellent thermal conductivity ensures uniform heat distribution, facilitating the solidification of molten metal within the mold cavity and promoting the formation of detailed and defect-free castings.
Furthermore, isostatic graphite blocks and molded graphite blocks contribute to environmental sustainability in the casting industry due to their long lifespan, minimal wear and tear, and recyclability. Their reliability and effectiveness in maintaining high precision and surface finish make them essential components in modern casting processes, enabling manufacturers to achieve greater efficiency and consistency in their production operations.
Isostatic graphite blocks and molded graphite blocks are indispensable assets in the casting industry, providing manufacturers with the means to achieve superior quality, precision, and productivity in the production of metal components. Their exceptional properties and versatility make them indispensable materials for a wide range of casting applications, contributing to the advancement of metal casting technology.
Graphite Mould for Casting Factors
There are many factors that determine the life of continuous casting graphite dies. The composition of casting material, to casting temperature, to cooling rate, will affect the life of graphite mold. The specific graphite grade used is also determined by a number of factors. The main factor is what kind of material technology is to be used in the graphite mould casting. For example, for gray cast iron or high-nickel alloys, wear-resistant graphite is required, while for brass, relatively dense graphite with sufficient porosity to allow zinc to evaporate would be a better choice.
Graphite Mold Casting Process
WH Graphite employs the highly efficient Graphite Permanent Mold Casting process, a metal casting technique renowned for its versatility and cost-effectiveness. This method utilizes durable graphite molds to produce a wide array of parts from metals like aluminum, zinc, and copper.
The process starts with mold preparation, where two carbon graphite blocks are secured in a press, and molten metal is poured into the mold's gate or injection cell. Once the metal solidifies, the graphite molds are separated, and the castings are carefully removed.
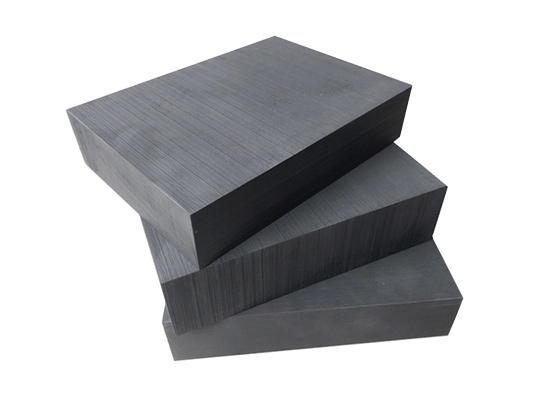

What sets this process apart is the reusable and long-lasting nature of graphite molds. The preparation of these molds involves creating a malleable paste by mixing graphite powder with a binder material, such as clay or resin, forming the mold.
Graphite mold casting offers several advantages, including reduced costs, extended mold life, and superior quality in the output parts. It finds applications across various industries, such as continuous casting, semi-continuous casting, and the casting of non-ferrous metals.
In summary, WH Graphite's Graphite Permanent Mold Casting is a valuable metal casting technology, offering high-quality metal parts, cost savings, and extended mold life, making it a crucial process for a wide range of applications.
Graphite Mold Casting Aluminum
Graphite mold casting for aluminum is a cost-effective and highly efficient metal casting process. This method involves the use of graphite molds to shape and cast aluminum parts. The process begins with the preparation of graphite molds, which are created by mixing graphite powder with a binder material. Once the molds are ready, molten aluminum is poured into them. As the aluminum cools and solidifies, it takes the form of the graphite mold, resulting in precise and high-quality aluminum components. Graphite mold casting for aluminum is renowned for its ability to produce intricate, detailed parts, its cost-efficiency, and its suitability for a wide range of applications in industries like automotive, aerospace, and more.
How to make graphite molds with casting
Making graphite molds for metal casting involves several steps and safety precautions to ensure a successful and safe process. Graphite, known for its heat resistance and lubricating properties, is an ideal material for creating molds due to its ability to withstand high temperatures without melting or deforming. Here's a comprehensive guide on how to make graphite molds with metal casting from WH Graphite Supplier:
Safety should always be the top priority when working with graphite and molten metal. Graphite dust can be harmful if inhaled, so it's crucial to use a HEPA filter dust collector during machining. Additionally, wearing safety glasses and gloves is essential to protect against dust and sharp edges. When handling molten metal, heat-resistant clothing and tongs are necessary to prevent burns.
The process begins with designing the mold cavity using 3D design software if needed. Once the design is finalized, obtain a solid block of graphite larger than the desired mold size. Use a CNC machine equipped with appropriate cutting tools to machine the graphite according to the design specifications. Features like draft angles and pouring sprue should be carefully considered during machining to ensure the successful casting of the metal.
For complex molds with multiple parts, assembly may be required. Machining grooves or inserts for a secure fit is essential to prevent any misalignment during casting.
It's important to note that machining graphite requires knowledge of CNC operation and proper cutting tool selection. Beginners should start with simpler mold designs to gain proficiency before attempting more complex projects. Additionally, for some metals, applying a mold coating may be necessary to improve surface finish or prevent reactions with the graphite.
Various resources are available to assist with graphite mold making, including video tutorials on YouTube and information from jeweler websites specializing in metal casting. By following these guidelines and taking necessary safety precautions, you can create high-quality graphite molds for metal casting with confidence.
 English
English